Factoring refers to a payment system, where a business sells the outstanding invoices to a third party (also called a factor) at a discount. This is an intermediary financing method to handle receivables and to optimize the working capital. In simple terms, it converts credit-sales to cash instantly.Under this arrangement, a factoring company takes ownership of the accounts receivable of the client and offers the advance, usually 80% of the value of the invoice (sometimes as much as 90%) on signing the contract. What is left (about 20 percent) less finance charges and service charges, is paid out to the client when the customer pays the invoice.
Collection of receivables collections can be done and managed by factor or by the client (depending upon nature of factoring deal e.g. recourse or non-recourse). Factoring has a wide range of application to both product based and service-based receivables.
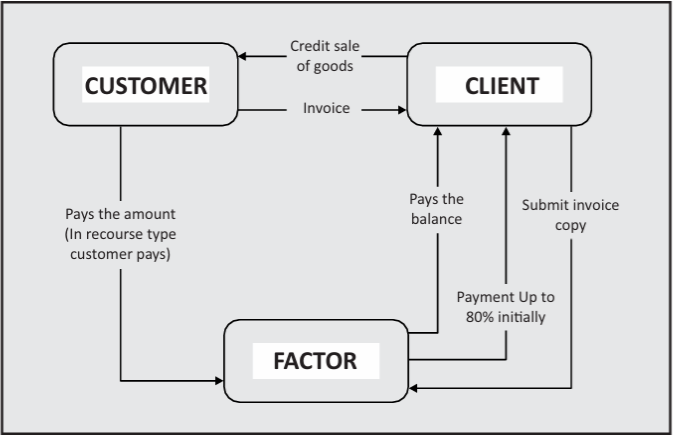
Important parties to a Factoring transaction
Seller: Offers goods and services and sends invoices to buyers.
Buyer: He/she is the receiver of goods/services and he/she makes payments.
Factor: A financial institution which provides funds to the seller against the invoices.
Process of Factoring:
1. Initial Contact
A seller goes to a broker or funding expert to state his need of funding.
2. Client Profiling
The broker will develop a client profile and present it to the prospective funders and request their consideration.
3. Preliminary Agreement
When factoring has appeared to be a good possibility, then the broker makes the seller directly meet the funder and discuss and negotiate a custom factoring plan with him.
4. Due Diligence
During the due diligence process, the seller might be required to pay legal costs. The factor will then analyze the credit quality of the buyer and inquire as to any legal encumbrance (e.g. UCC filings, judgments, liens) on the sellers account receivables.
5. Looking at Notification and Documentation
The seller informs the buyer of existence of the factoring contract through a formal letter.An acknowledged copy by the buyer is presented to the factor (note: the permission by the buyer is not mandatory).The factor also issues a sanction letter to the seller and this letter spells terms and needs to be signed after acceptance.
6. Sanction Letter should Contain:
Facilities covered
Validity period.
Factoring effective date (e.g. only invoices dated since a particular date would be eligible).
Authorized persons to submit the invoices.
Credit limits.
The buyer advised confirmation.
7. Discounting and charges:
The factor charged on a discount/ fee rate.The explanation of any discount that the sellers give to the buyers and the way it influences the sum of the financed money.
8. Execution7-10 days:
Signing of agreements, filing of UCC forms, notification of buyers and first advance are made.Advance normally goes between:Generally in the invoices, the percent of its value 70-80.60 70 per cent in construction.The rest is kept (reserved) until the buyer pays.
9. Invoicing and financing
Seller fulfils the delivery or service and issues invoices.Invoices are sent (e.g. by fax or by email) to the factor.When verified, the negotiated advance is then wired to the seller, which may even come at a charge (at times).
10. Payment and Settlement
The factor is paid by buyer.The factor is given the payment and on receiving the payment deducts their amount and the balance of the reserve is sent to the seller.